|
FM_DOP
FM Doppler Systems
Blood Velocity Estimation with Frequency Modulated Ultrasound
This project investigates the applicability of coherent, linearly frequency modulated (FM)
excitation signals for blood velocity measurements. Systems based on such excitation signals are
called FM Doppler systems.
By utilizing FM signals, it is possible to avoid the high peak energy emitted with
conventional pulsed wave Doppler systems. In an echo-ranging system, everything
else equal, the range resolution size is inversely proportional to the bandwidth of the emitted
signal. Thus, if the range resolution is to be improved in a PW Doppler system, the time duration of
the emitted burst must be reduced. On the other hand, if the signal to noise ratio is to remain
unchanged, the mean emitted power must also be kept constant, which requires increased peak
emitted power. However, from a design point of view, a high peak to average power is
undesirable, as the duty cycle diminish and non-linear propagation may occur. In addition,
especially for medical applications, the peak power level might in certain situations exceed the
regulatory limits for diagnostic ultrasound equipment.
We have shown that the signal processing principles, utilized with Pulsed Wave - time shift measurement Doppler (PW-tsm),
can be used with FM excitation signals as well. The FM counterpart to the
PW-tsm technique is spectral cross-correlation, and such a system is called Frequency Modulation -
frequency shift measurement, FM-fsm.
Experimental data, recorded at Worcester Polytechnic Institute, has been processed with an improved version of the fsm
signal processing technique. The promising results show that the FM technique has a precision
comparable to that of the PW technique.
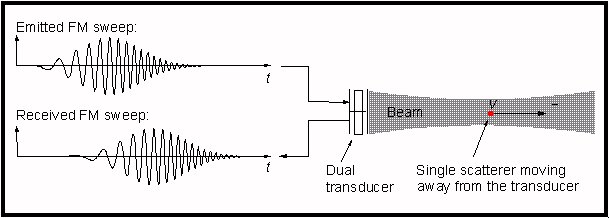
An example of the emitted and received FM sweep from a single point target is given in the figure below. The envelope
of the emitted signal is Gaussian.
Further information from:
© 1996 - 2012 by Jens E. Wilhjelm, DTU Elektro
No material obtained from this homepage may be used commercially without written permission.
|